What is Swiss Machining?
In today's rapidly evolving manufacturing landscape, the demands for machining precision, consistency, and delivery efficiency are higher than ever.
Medical implants require micron-level accuracy, electronic connectors demand exceptional batch consistency, and aerospace parts must achieve lightweight structures using high-strength materials. Swiss Machining is once again at the center of attention as a key manufacturing solution.
As a manufacturer deeply involved in the practical application of precision machining technologies, Minnuo aims to help you truly understand what Swiss machining is, how to select the right solution, how to maximize machining efficiency, and how to match machine structure to specific part characteristics.

1. What Exactly Is Swiss Machining?
Swiss machining is a high-precision turning method based on a sliding headstock combined with a guide bushing support. Unlike conventional lathes, a Swiss-type CNC lathe allows the bar stock to move axially during the machining process, while the cutting tools are fixed close to the cutting zone. This design ensures stronger support and significantly reduces deflection.This structure is ideal for:
•Long, slender, small-diameter parts
•Complex geometries
•Parts requiring front and back machining in one cycle
•Applications demanding high consistency in batch production
2. Why Is It Called “Swiss” Machining?
Swiss machining originated in 19th-century Switzerland to serve the watchmaking industry, which required miniature, complex, and highly consistent parts. The Swiss developed a special lathe structure to meet these needs.Today, this has evolved into the modern CNC Swiss Machine, equipped with:
•Servo-driven and CNC-controlled systems
•Multi-axis control and live tooling functions
•Core equipment across high-precision manufacturing industries worldwide
Regardless of how the technology has advanced, its fundamental mission remains unchanged: to produce small, complex parts with high precision, high speed, and excellent repeatability.
3. Core Principle of Swiss Machining
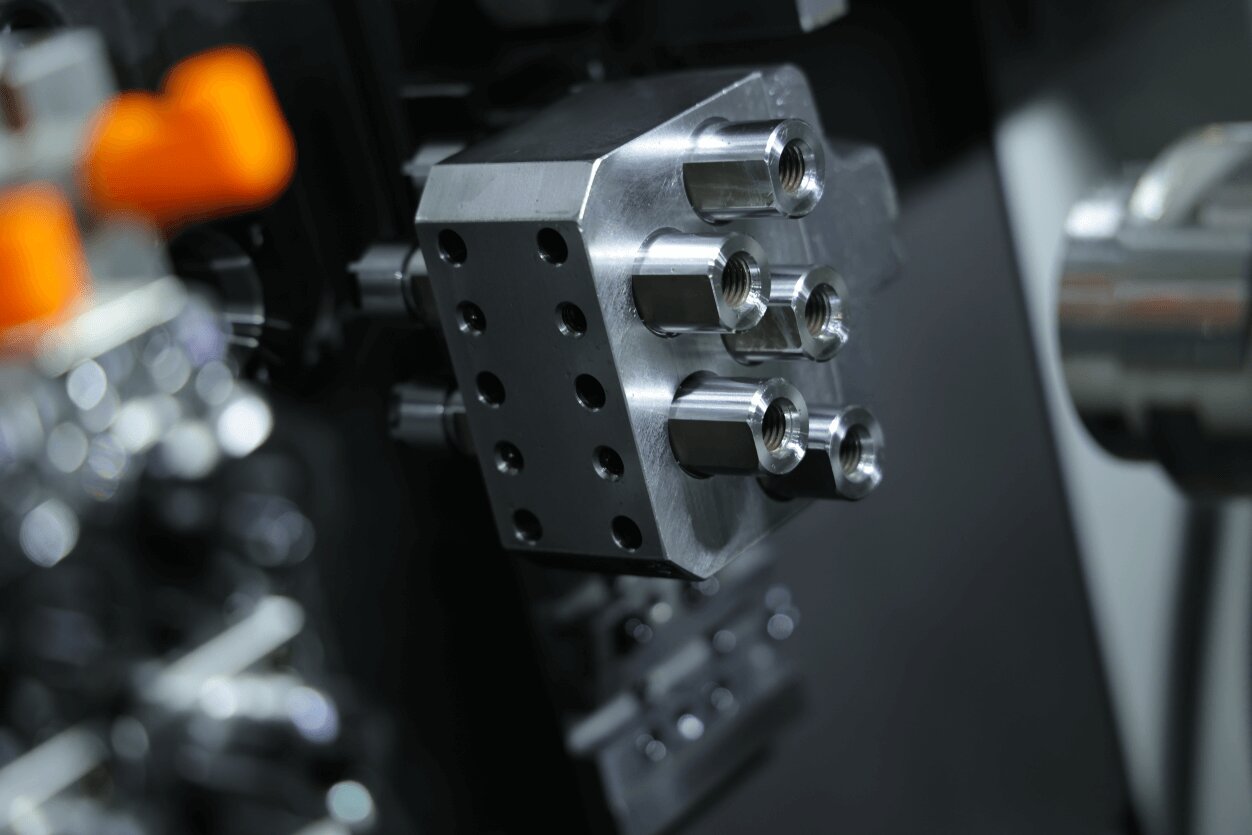
A typical Swiss lathe configuration includes:
•Main spindle + sub-spindle: for simultaneous front and back operations
•Guide bushing: critical for vibration suppression and precise support
•Multiple tool stations: front tools, back tools, and live tools working together
•Sliding headstock: dynamically controls bar feed and cutting paths
•Automatic bar feeder / part catcher: enabling unmanned, continuous operation
In our project designs, we often combine sub-spindles with backworking stations to help customers convert multi-operation parts into one-pass finished components—significantly reducing machining time and manual handling.
4. The Advantages of Swiss-Type Machines Go Far Beyond Just Precision
Advantage | Practical Value |
thermal error compensation to achieve stable tolerance control at ±0.002 mm | Meets strict standards for medical and aerospace parts |
Powerful one-pass processing capability | Eliminates secondary operations for complex geometries |
Concurrent operations, shorter cycle time | Back tools work simultaneously; 30–50% time savings |
High automation compatibility | Integrates with bar feeders and robots for 24/7 operation |
Space and labor savings | Higher output in the same footprint; fewer operators needed |
In a real Minnuo project, we helped an automotive components manufacturer consolidate a process previously done on two conventional lathes + one transfer step into a single Swiss-type machine operation. This not only halved the cycle time but also freed up manpower for higher-value tasks.
5. Recommended Materials for Swiss Machining
Material Type | Typical Applications |
Medical-grade stainless steel (316L, 17-4PH) | Orthopedic screws, dental implants |
Titanium alloys (Gr5) | Bone plates, aerospace connectors |
Aluminum alloys | Electronic housings, structural components |
Brass, copper | RF connectors, electronic terminals |
PEEK, Delrin | High-insulation components |
Inconel, Monel and other superalloys | Jet engine components |
Tip: Guide bushing systems require high bar straightness. During factory setup, we always conduct material matching tests and recommend centerless ground bar stock for optimal performance.
6. Industries Best Suited for Swiss Machining

Industry | Typical Parts |
Medical Devices | Screws, needles, catheter hubs, implants |
Aerospace | Connectors, valve cores, fuel control components |
Automotive | Solenoid shafts, sleeves, sensor pins |
Electronics & Telecom | Micro plugs, RF connectors |
Precision Watchmaking | Shafts, crowns, escapement components |
Minnuo has delivered Swiss machining solutions across all these industries, from prototype testing to full-line integration, ensuring each machine is not only running—but delivering measurable value on the production floor.
7. Key Differences: Swiss Machining vs Conventional Turning
Item | Swiss Machining | Conventional Turning |
Workpiece Support | Guide bushing near the cut for high stability | Single-end clamping; more prone to deflection |
Precision Control | Higher (±0.002mm) | Moderate (±0.01mm) |
Cycle Time | Faster with multi-tool simultaneous cutting | Slower; sequential operations |
Structural Complexity | Handles multiple features in one setup | Often requires multiple operations |
Automation Level | High; suitable for unmanned operation | Moderate; more manual intervention |
8. 5 Key Considerations Before Investing in Swiss Machining

•Is your production volume sufficient?
A few hundred pieces per month and up can justify the investment.
•Are your parts structurally complex?
If there are back operations, cross-holes, angled surfaces, or threads—Swiss is ideal.
•Do you have programming capability?
Swiss machines require multi-channel programming. Minnuo provides process and CAM support for our customers.
•Is your coolant & filtration system up to par?
These directly impact surface finish and tool life.
•Do you plan to run lights-out production?
Choose the right bar feeder + part catcher to maximize ROI through automation.
9. Conclusion
Swiss machining is no longer a niche choice for watchmakers—it has become a systematic response to modern demands for precision, efficiency, and automation. It not only improves yield and cycle time but also plays a central role in digital and flexible manufacturing systems.At Minnuo, we combine Swiss machining principles with real-world production needs to deliver not just machines—but complete, practical solutions that perform on the shop floor.
Want to know if your parts are suitable for Swiss machining? Looking for the most cost-effective machine configuration? We’re here to help—with experience you can rely on.

 Email
Email sales1:+1 213 865 6527
sales1:+1 213 865 6527 


