Exploring Different Types of Grinding Machines
How do manufacturers achieve such precision in creating complex components? What makes grinding machines so essential across industries like automotive, aerospace, and metalworking?
Grinding machines come in a variety of types, each tailored for specific tasks. The most widely used types of grinding machines include surface grinders, cylindrical grinders, centerless grinders, and tool grinders. Each machine serves a unique purpose, whether it's for achieving smooth surfaces, creating precise cylindrical shapes, or sharpening cutting tools.
Let’s dive into the grinding technologies that fuel industrial progress.
Ⅰ.Types of Grinding Machines
1.Cylindrical Grinder
The cylindrical grinder specializes in external cylindrical grinding, ideal for parts of various diameters and lengths.
Working Principle: The workpiece is rotated while securely clamped at the center, and the grinding wheel moves along the axis to shape the part
Features: High precision, mass production capabilities, and versatility in automotive, aerospace, and mechanical manufacturing.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, ranging from $1,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Grinding automotive engine shafts, bearings, and precision mechanical components.
2.Surface Grinder

Surface grinders are designed for precision flat grinding, ensuring surface flatness and accuracy.
Working Principle: The workpiece is held on a worktable, while the grinding wheel moves horizontally to grind the surface.
Features: High surface smoothness, stable precision, perfect for molds, templates, and mechanical part manufacturing.
Price Range: Mid to high-end, ranging from $100 to $10,000.
Applications: Surface finishing of molds, precise grinding and finishing of flat components.
3.Form Grinder
Form grinders are designed for grinding complex-shaped workpieces.
Working Principle: This machine grinds workpieces based on preset profiles, providing precise shapes.
Features: Ideal for manufacturing intricate shapes and parts with high precision.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, ranging from $1,000 to $100,000
Applications: Precision machining of complex parts and special-shaped components.
4.Jig Grinder
Jig grinders are specialized for precise machining of workpieces fixed securely on jigs.
Working Principle: Workpieces are fixed on a jig, and the grinding wheel grinds precisely under controlled conditions
Features: High precision and excellent repeatability, ideal for molds, templates, and other high-precision parts.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, ranging from $1,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Precision surface and internal machining of molds and fine parts.
5.Hand Grinder
Portable hand grinders are designed for rough grinding or polishing tasks.
Working Principle: The operator manually holds and moves the grinding or polishing wheel for processing
Features: Flexible, portable, and easy to use for small parts repair and DIY projects.
Price Range: Low to mid-range, ranging from $10 to $100.
Applications: Ideal for home repairs, light metalworking, and small woodworking projects.
6.Thread Grinder
Thread grinders are built for the precise machining of various types of threads.
Working Principle: The grinding wheel is precisely controlled to shape threads on workpieces.
Features: High precision, excellent repeatability, suitable for producing accurate threads.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, ranging from $1,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Machining threads for automotive components, mechanical parts, and instruments.
7.Centerless Grinder
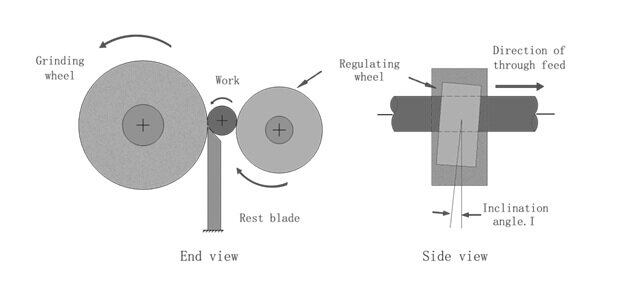
The centerless grinder operates without the need to center the workpieces, using a work rest and regulated wheel for grinding.
Working Principle: The workpiece is supported by a rest, while both the grinding and regulating wheels shape the part.
Features: Efficient and suitable for long, slender workpieces like shafts and bearings.
Price Range: Mid-range, typically $1,000 to $10,000.
Applications: Used in automotive, aerospace, and engineering industries for machining shafts and other cylindrical parts.
8.Belt Grinder
Belt grinders use abrasive belts for rough grinding and finishing operations.
Working Principle: The machine uses an abrasive belt to polish, grind, or finish metal and wood surfaces.
Features: Fast and efficient, excellent for large surface treatments.
Price Range: Low to mid-range, $100 to $1,000.
Applications: Metalworking, woodworking, and mold finishing
9.Angle Grinder
Angle grinders are handheld tools used for cutting, grinding, and polishing metals.
Working Principle: The operator controls the grinding wheel for various tasks in construction and metalworking.
Features: Highly flexible and multi-functional for various grinding and cutting applications.
Price Range: Low to mid-range, $10 to $100.
Applications: Construction, workshop maintenance, and DIY projects.
10.Double Column Surface Grinder
This grinder is specifically designed for large workpieces with stable processing capabilities.
Working Principle: The workpiece is held between double columns, while the grinding wheel moves horizontally across the surface.
Features: Used for large molds and mechanical parts.
Price Range: High-end, ranging from $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Large molds, ship components, and aerospace parts machining.
11.Cryogenic Grinding Machine
Cryogenic grinders use low temperatures to process materials that are difficult to handle at room temperature.
Working Principle: Grinding occurs at low temperatures to reduce heat effects and prevent material deformation.
Features: Suitable for plastics, rubber, and powder metallurgy materials.
Price Range: High-end, typically $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Food processing, chemicals, and pharmaceutical industries for fine grinding.
12.Internal Grinder

Internal grinders are designed for machining the internal surfaces of workpieces.
Working Principle: The grinding wheel enters the workpiece to perform precise internal grinding.
Features: High precision for small and deep hole machining.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Automotive, aerospace, and precision mechanical shaft parts machining.
13.Universal Grinder
Universal grinders are capable of performing a variety of grinding operations.
Working Principle: Designed for external, internal, flat, and special-shaped workpieces.
Features: Highly adaptable, meeting diverse machining needs.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: General mechanical manufacturing, multi-functional parts machining.
14.Gear Grinder
Gear grinders are specifically used for machining precision gears.
Working Principle: The grinding wheel is controlled to grind gears with high precision.
Features: High precision and stability, ideal for automotive and industrial gears.
Price Range: Medium to high-end, $1,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Transmission devices, mechanical transmission components.
15. Bench Grinder
A simple grinder that sits on a bench.
Working Principle: Turn a wheel or flip a switch to turn the grinding wheel on and off to grind and finish workpieces.
Features: Easy to use, ideal for grinding and fixing small pieces of metal and wood.
Price Range: Affordable, typically $20 to $100, though high-end models can cost a few hundred dollars.
Applications: Perfect for home shops, school labs, or light repair work.
16. Horizontal Spindle Grinder
A grinder with a horizontal spindle designed for grinding large, flat items and shafts.
Working Principle: The grinding wheel moves back and forth across the part's surface, grinding flat surfaces and shafts.
Features: Suitable for grinding large molds, ship parts, and heavy mechanical components.
Price Range: Expensive, ranging from $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Used in aerospace, shipbuilding, and heavy machinery manufacturing to grind large parts.
17. Precision Grinder
A grinder designed for ultra-precise work.
Working Principle: Uses highly accurate control of the grinding wheel to grind parts to within a few millionths of an inch.
Features: Ideal for making parts with very high accuracy and excellent surface finishes.
Price Range: High-end, typically $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Used in optical, electronics, and medical device industries for precision components.
18. Dry Grinder
A grinder that operates without coolant.
Working Principle: Uses abrasive tools to grind and finish workpieces without the need for coolant.
Features: Energy-efficient and environmentally friendly, effective for grinding metals and non-metallic materials.
Price Range: Affordable, typically between a few hundred to a few thousand dollars.
Applications: Ideal for mold making, templates, and general metal grinding without coolant.
19. Flexible Grinder
A versatile grinder capable of performing various tasks.
Working Principle: Can be used in many different ways for various tasks on different parts.
Features: Flexible and adaptable, suitable for various production environments.
Price Range: Expensive, typically ranging from $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Commonly used in the automotive industry, aerospace, and general machine shops for versatile tasks.
20. Tool Grinder

A grinder for making and sharpening tools.
Working Principle: Uses precise control to grind and regrind tools for various purposes.
Features: Maintains tool accuracy and prolongs their lifespan.
Price Range: Expensive, generally $10,000 to $20,000.
Applications: Used to make and fix tools for machine tools, molds, woodworking, and cutting tools.
21. Center Grinder
A grinder specifically designed for making centers.
Working Principle: Grinds and trims centers to ensure parts are in the correct position and quality.
Features: Ideal for making centers used in tool and mold manufacturing.
Price Range: Expensive, typically $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Used to create and trim centers for molds and mechanical parts.
22. Plunge-Cut Grinder
A grinder used for grinding deep holes through plunging.
Working Principle: The grinding wheel plunges into the part to grind deep, accurate holes.
Features: Excellent for grinding deep and accurate holes, ensuring the part maintains the correct shape both inside and outside.
Price Range: Expensive, typically ranging from $10,000 to $100,000.
Applications: Used to grind deep holes in molds and engine parts, especially in the automotive industry
Ⅱ.How to Choose a Grinding Machine
Selecting the right grinding machine requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure it meets both your immediate and long-term production needs. Here's a comprehensive guide to help you make an informed decision:
Determine Your Processing Needs: Understand the types of tasks you'll be performing, such as grinding specific materials or achieving precise shapes.
Choose the Type of Grinding Machine: Depending on your needs, decide between surface grinders, cylindrical grinders, or centerless grinders.
Evaluate Precision and Repeatability: Look for machines that offer stable precision and excellent repeatability to maintain high-quality output.
Consider Cost-Effectiveness: Weigh the machine's purchase price, maintenance costs, and energy efficiency.
Seek Reliable Technical Support: Choose a supplier with excellent after-sales service and technical support to ensure smooth operation and maintenance.
Conclusion
Grinding machines are an integral part of the modern manufacturing process. From simple handheld grinders to advanced CNC-operated machines, each type serves a distinct purpose, ensuring the production of high-quality, precision parts. Whether you're involved in automotive, aerospace, or metalworking, selecting the right grinding machine is key to meeting industry standards and achieving operational success.
If you need more information or assistance in choosing the right grinding machine for your needs, feel free to contact us!

 Email
Email sales1:+1 213 865 6527
sales1:+1 213 865 6527 


